Sociological Analysis of the Elderly through an Interview

Welcome to The Knowledge Nest, your go-to resource for insightful discussions and analysis of various societal aspects. In this article, we delve into a comprehensive sociological analysis of the elderly through an in-depth interview. Our aim is to provide valuable insights into the challenges, experiences, and social aspects of aging.
1. Understanding the Elderly Population
The elderly population, also known as seniors or senior citizens, refers to individuals who have reached a certain age threshold, typically 65 years and above. This stage of life is characterized by unique experiences, physical changes, and social interactions that shape their overall well-being.
1.1. Demographic Trends
Before delving into the sociological analysis, it is essential to understand the demographic trends surrounding the elderly population. According to recent studies, the number of elderly individuals has been steadily increasing over the years, reflecting a global phenomenon. Factors such as increased life expectancy and declining birth rates contribute to this growing segment of the population.
1.2. Societal Perceptions and Stereotypes
Societal perceptions and stereotypes about the elderly can significantly impact their quality of life. Often, negative stereotypes portray them as frail, forgetful, and burdensome. Through the interview conducted by The Knowledge Nest, we aim to challenge these stereotypes and shed light on the diverse realities of the elderly population.
2. Methodology
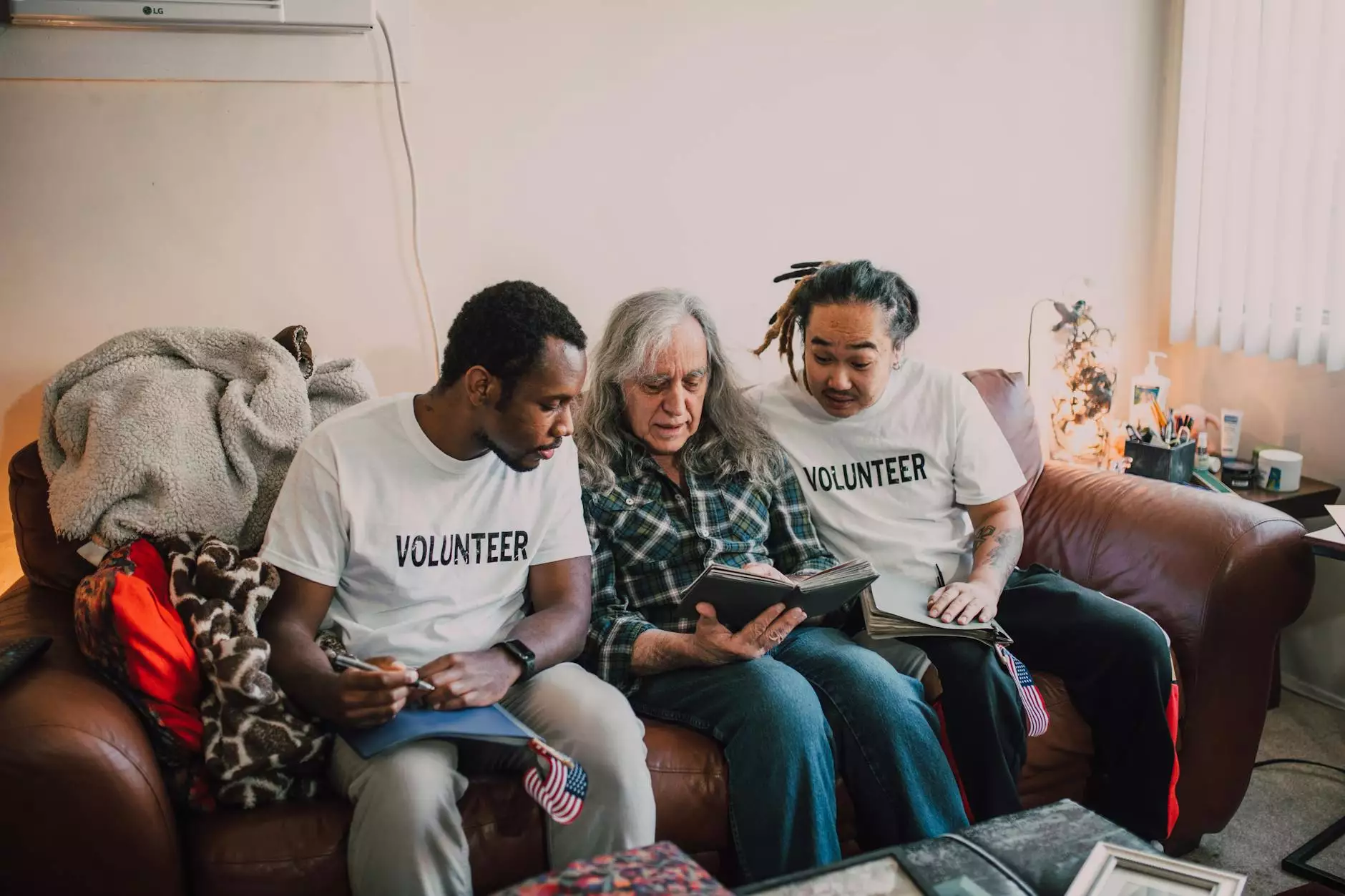
At The Knowledge Nest, we believe in thorough research and analysis. To conduct this sociological analysis, we employed a combination of qualitative research methods, focusing on an in-depth interview with elderly individuals residing in different geographical locations.
2.1. Selection Process
The selection process was designed to ensure diverse representation, considering factors such as gender, socioeconomic background, and cultural diversity. This approach allowed us to capture a wide range of perspectives and experiences within the elderly population.
2.2. Interview Structure
The interview followed a structured approach, with a series of questions designed to explore various aspects of the participants' lives. These questions covered areas such as social interactions, health and well-being, family dynamics, and societal support systems.
3. Key Findings
The key findings derived from the sociological analysis provide in-depth insights into the lives of the elderly population. These findings challenge existing societal notions and offer a more nuanced understanding of the challenges and experiences faced by the elderly.
3.1. Social Isolation and Loneliness
One of the recurrent themes that emerged from the interviews was the prevalence of social isolation and loneliness among the elderly. The participants highlighted how societal changes, such as migration of younger generations and changing family structures, have contributed to a lack of social connections.
3.2. Resilience and Adaptability
Contrary to popular beliefs, our analysis revealed the immense resilience and adaptability exhibited by the elderly population. Despite facing various challenges, such as declining physical health, they showcased a remarkable ability to adapt to changing circumstances and find joy in simple pleasures.
3.3. Interdependence and Community Support
The interviews also shed light on the importance of community support and interdependence among the elderly population. Participants unanimously emphasized the significance of social networks, community engagement, and access to supportive services in enhancing their overall well-being.
4. Implications and Recommendations
Based on the comprehensive sociological analysis, we propose the following implications and recommendations to improve the well-being of the elderly population:
4.1. Strengthening Social Programs
It is crucial to invest in robust social programs that facilitate social interactions, encourage active engagement, and address the issue of social isolation among the elderly. These programs should be inclusive, accessible, and cater to the diverse needs of the elderly population.
4.2. Fostering Intergenerational Connections
Promoting intergenerational connections and interactions can be highly beneficial for both younger and older generations. Initiatives that facilitate intergenerational activities, such as mentorship programs and community events, can help bridge the gap between different age groups.
4.3. Raising Awareness and Challenging Stereotypes
Creating awareness about the diverse experiences and capabilities of the elderly population is crucial to challenge negative stereotypes and promote a more inclusive society. Education campaigns and media initiatives can play a significant role in reshaping societal perceptions.
As The Knowledge Nest, our commitment to providing comprehensive and insightful analysis extends to various aspects of society. Through this sociological analysis of the elderly population, we aim to contribute to the broader discourse surrounding aging and promote a better understanding and appreciation for the challenges faced by the elderly.