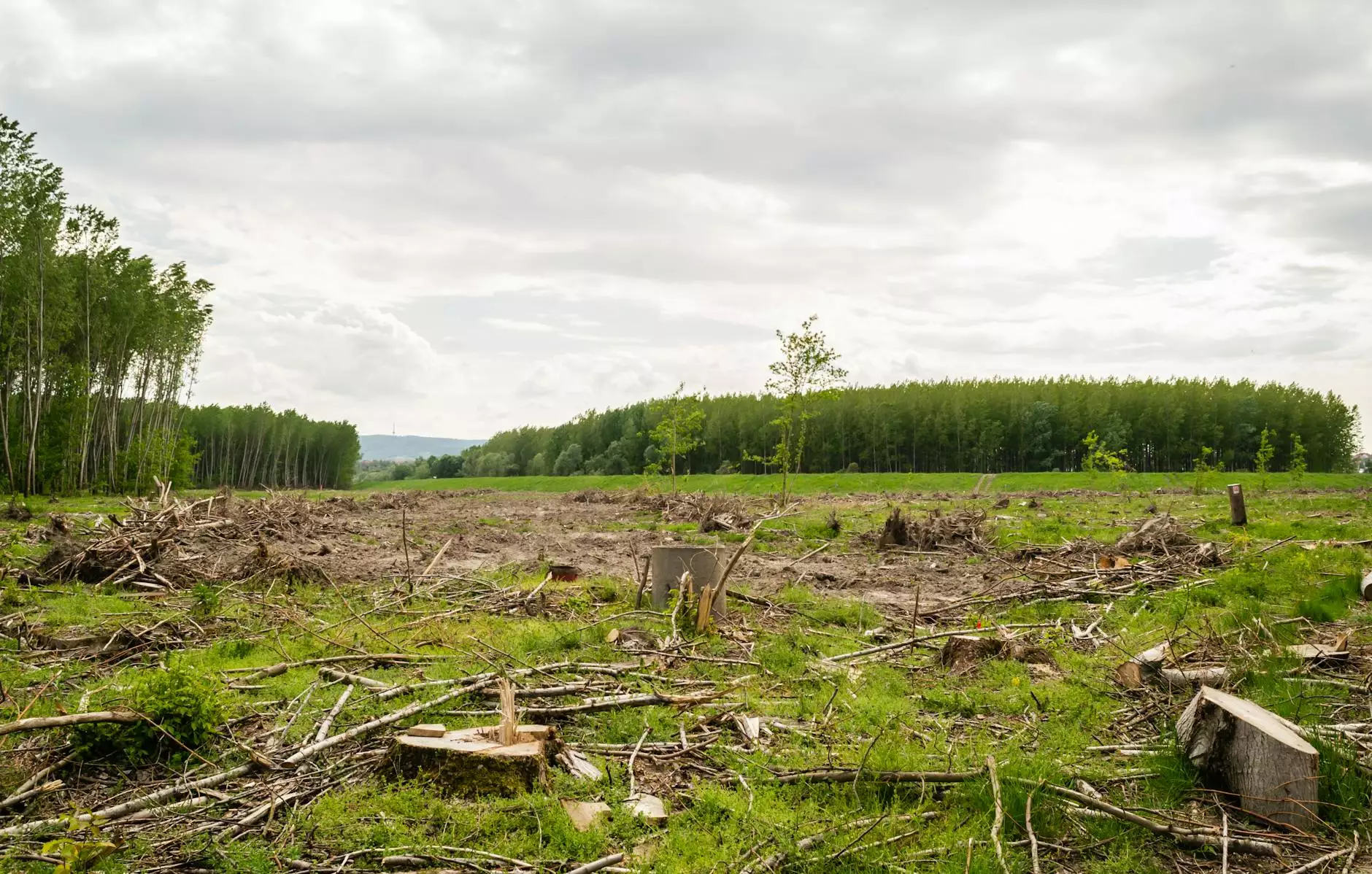
DEFORESTATION IN INDIA

Welcome to The Knowledge Nest, your go-to resource for in-depth information on a wide range of topics. In this research paper example, we delve into the issue of deforestation in India, exploring its causes, impacts, and potential solutions. By understanding the gravity of this environmental crisis, we can work towards devising strategies to mitigate its adverse effects on both the environment and society.
Deforestation in India: A Threatening Reality
Deforestation, the permanent destruction of forested areas, not only compromises the natural habitat of countless species but also poses severe consequences for communities and society at large. In India, a country blessed with diverse ecosystems and rich biodiversity, deforestation is a growing concern that demands immediate attention.
Causes of Deforestation in India
Multiple factors contribute to deforestation in India. One of the primary causes is the expansion of agricultural land to meet the rising food demands of a growing population. The need for infrastructure development, such as roads and highways, also leads to the clearing of forests in many regions.
Illegal logging, driven by the lucrative timber trade, further exacerbates the problem. Additionally, forest fires, often a result of human activities or natural causes, contribute significantly to deforestation. These combined factors create an alarming scenario that calls for effective measures to combat deforestation in India.
Impacts of Deforestation in India
The consequences of deforestation in India are far-reaching and affect various aspects of the environment and society. The loss of forest cover disrupts the delicate ecological balance, leading to decreased biodiversity and the potential extinction of numerous plant and animal species.
Moreover, deforestation contributes to climate change, as trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. With fewer trees, the concentration of greenhouse gases increases, causing global warming and negative climate effects, such as unpredictable weather patterns and rising temperatures.
Deforestation also has significant socio-economic impacts. Indigenous communities relying on forests for their livelihoods face displacement and loss of cultural heritage. Furthermore, the loss of forest resources affects the availability of essential products like timber, medicinal plants, and non-timber forest products, leading to economic hardships and increased poverty levels.
Solutions to Deforestation in India
Tackling deforestation in India requires a multi-faceted approach that combines policy interventions, community engagement, and sustainable practices. The government can play a crucial role by implementing stricter regulations against illegal logging and promoting initiatives aimed at restoring degraded forests.
Encouraging sustainable agriculture practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry, can help reduce the need for expanding agricultural land into forests. Reforestation efforts, aimed at planting new trees and restoring damaged ecosystems, serve as vital tools in combating deforestation and mitigating its impacts.
Community participation and awareness are also essential in the fight against deforestation. Educating local communities about the importance of forests, providing alternative livelihood options, and empowering them to actively participate in forest management can yield long-term sustainable solutions.
Conclusion
Deforestation in India presents a challenging problem that requires urgent action from all stakeholders. By understanding the causes, impacts, and potential solutions to this alarming crisis, we can work towards preserving our forests, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring a sustainable future for both the environment and society.